Remote Control Airplanes
HAM Radio
Commercial Radio
ISM
industrial-scientific-medical frequency band
industrial-scientific-medical frequency band
Wireless Internet
Bluetooth
Wi-Fi
Television
Miscellaneous
|
27 MHZ |
|
|---|---|
| Ch | Freq |
| A1 | 26.995 |
| A2 | 27.045 |
| A3 | 27.095 |
| A4 | 27.145 |
| A5 | 27.195 |
| A6 | 27.255 |
|
50 MHZ |
|
|---|---|
| Ch | Freq |
| 00 | 50.800 |
| 01 | 50.820 |
| 02 | 50.840 |
| 03 | 50.860 |
| 04 | 50.880 |
| 05 | 50.900 |
| 06 | 50.920 |
| 07 | 50.940 |
| 08 | 50.960 |
| 09 | 50.980 |
| 72 MHZ Aircraft Only |
|
|---|---|
| Ch | Freq |
| 11 | 72.010 |
| 12 | 72.030 |
| 13 | 72.050 |
| 14 | 72.070 |
| 15 | 72.090 |
| 16 | 72.110 |
| 17 | 72.130 |
| 18 | 72.150 |
| 19 | 72.170 |
| 20 | 72.190 |
| 21 | 72.210 |
| 22 | 72.230 |
| 23 | 72.250 |
| 24 | 72.270 |
| 25 | 72.290 |
| 26 | 72.310 |
| 27 | 72.330 |
| 28 | 72.350 |
| 29 | 72.370 |
| 30 | 72.390 |
| 31 | 72.410 |
| 32 | 72.430 |
| 33 | 72.450 |
| 34 | 72.470 |
| 35 | 72.490 |
| 36 | 72.510 |
| 37 | 72.530 |
| 38 | 72.550 |
| 39 | 72.570 |
| 40 | 72.590 |
| 41 | 72.610 |
| 42 | 72.630 |
| 43 | 72.650 |
| 44 | 72.670 |
| 45 | 72.690 |
| 46 | 72.710 |
| 47 | 72.730 |
| 48 | 72.750 |
| 49 | 72.770 |
| 50 | 72.790 |
| 51 | 72.810 |
| 52 | 72.830 |
| 53 | 72.850 |
| 54 | 72.870 |
| 55 | 72.890 |
| 56 | 72.910 |
| 57 | 72.930 |
| 58 | 72.950 |
| 59 | 72.970 |
| 60 | 72.990 |
|
75 MHZ |
|
|---|---|
| Ch | Freq |
| 61 | 75.410 |
| 62 | 75.430 |
| 63 | 75.450 |
| 64 | 75.470 |
| 65 | 75.490 |
| 66 | 75.510 |
| 67 | 75.530 |
| 68 | 75.550 |
| 69 | 75.570 |
| 70 | 75.590 |
| 71 | 75.610 |
| 72 | 75.630 |
| 73 | 75.650 |
| 74 | 75.670 |
| 75 | 75.690 |
| 76 | 75.710 |
| 77 | 75.730 |
| 78 | 75.750 |
| 79 | 75.770 |
| 80 | 75.790 |
| 81 | 75.810 |
| 82 | 75.830 |
| 83 | 75.850 |
| 84 | 75.870 |
| 85 | 75.890 |
| 86 | 75.910 |
| 87 | 75.930 |
| 88 | 75.950 |
| 89 | 75.970 |
| 90 | 75.990 |
|
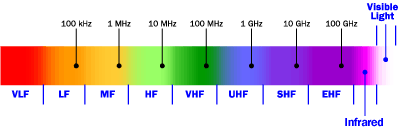
Medium Frequency (MF) (300 kHz to
3 MHz)
High Frequency (HF) (3.0 - 30.0 MHz) Very High Frequency (VHF) (30 to 300 MHz) Ultra High Frequency (UHF) (300 MHz to 3 GHz) Super High Frequency (SHF) (3 to 30 GHz) Extremely High Frequency (EHF) (30 to 300 GHz) |
|
|---|---|
|
Through
ITU (International Telecommunication Union) agreement bandwidth
has been set aside for amateur transmissions. Amateurs use a variety
of transmission modes, including Morse code, radio teletype, data,
and voice. Specific frequency allocations are a matter of record
and vary from country to country and region to region, but the frequency
allocations in the USA are:
Medium Frequency (MF) (300 kHz to 3 MHz) 160 metres (1.8 - 2.0 MHz) High Frequency (HF) (3.0 - 30.0 MHz) 80 metres (3.5 - 4.0 MHz) 60 metres (five USB voice channels: 5.332, 5.348, 5.368, 5.373, 5.405 MHz) 40 metres (7.0 - 7.3 MHz) 30 metres (10.100 - 10.150 MHz) 20 metres (14.000 - 14.350 MHz) 17 metres (18.068 - 18.168 MHz) 15 metres (21.000 - 21.450 MHz) 12 metres (24.890 - 24.990 MHz) 10 metres (28.0 - 29.7 MHz) Very High Frequency (VHF) (30 to 300 MHz) 6 metres (50 - 54 MHz) 2 metres (144 - 148 MHz) 1.25 metres (222 - 225 MHz) Ultra High Frequency (UHF) (300 MHz to 3 GHz) 70 centimetres (420 - 450 MHz) 33 centimetres (902 - 928 MHz) 23 centimeters (1.24 - 1.3 GHz) 13 centimeters (2.30 - 2.31 GHz and 2.39 - 2.45 GHz) Super High Frequency (SHF) (3 to 30 GHz) 9 centimetres (3.3 - 3.5 GHz) 5 centimetres (5.65 - 5.925 GHz) 3 centimetres (10.0 - 10.5 GHz) 1.2 centimetres (24.00 - 24.25 GHz) Extremely High Frequency (EHF) (30 to 300 GHz) 6 millimetres (47.0 - 47.2 GHz) 4 millimetres (75.5 - 81.0 GHz) 2.5 millimetres (119.98 - 120.02 GHz) 2 millimetres (142 - 149 GHz) 1 millimetre (241 - 250 GHz) The ARRL has a detailed band plan (http://www.arrl.org/FandES/field/regulations/bandplan.html) on their website. For ITU region 2, RSGB's band plan (PDF) (http://www.rsgb.org/bandplans/bandplans.pdf) will be more definitive. |
| 88-108 MHZ 87.5
to 108 megahertz (MHz) - also known as VHF Band II
|
|---|
| 902-928 MHz, 2400-2483 MHz, 5725-5780 MHz |
|
|---|---|
| Description | Freq |
| Cordless Phone | 43-50 MHz 900 MHz-2.4Ghz DSS |
| 2400 - 2 483.5 MHz 2 layers |
|---|
| 2402 - 2480 MHz with 79 1-MHz RF channels |
|
|---|---|
|
Generally,
small handhelds like the palm, and most new macintosh computers
use "bluetooth" as a means of exchanging data within 30 feet. It
enables users to connect a wide range of computing and telecommunications
devices easily and simply, without the need to buy, carry, or connect
cables.
It uses the 2.4 ghz spectrum to communicate a 1 megabit connection between 2 devices for both a voice channel and a 768k data channel The entire channel has a total capacity of 1 megabit per second (Mbps). Headers and handshaking information consume about 20 percent of this capacity. In the United States and Europe, the frequency range is 2,400 to 2,483.5 MHz, with 79 1-MHz radio frequency (RF) channels. In practice, the range is 2,402 MHz to 2,480 MHz. In Japan, the frequency range is 2,472 to 2,497 MHz with 23 1-MHz RF channels. A data channel hops randomly 1,600 times per second between the 79 (or 23) RF channels. Each channel is divided into time slots 625 microseconds long. A piconet has a master and up to seven slaves. The master transmits in even time slots, slaves in odd time slots. Packets can be up to five time slots wide. Data in a packet can be up to 2,745 bits in length |
| 2.4 and 5 GHz 2 channels |
|
|---|---|
|
General
Wi-Fi routers contains dual bands for transmitting the 802.11 standard
across the 2.4 and 5 GHz spectrums.
|
| VHF and UHF | |
|---|---|
|
VHF
The general services in the VHF band are: 30-46 MHz: Licensed 2-way land mobile communication 30-88 MHz: Military VHF-FM, including SINCGARS 46-50 MHz: Cordless telephones, "49 MHz" FM walkie-talkies, and mixed 2-way mobile communication 50-54 MHz: Amateur radio "6-meter" band 54-72 MHz: TV channels 2, 3, and 4 72-76 MHz: Remote Control devices 76-88 MHz: TV channels 5 and 6 88-108 MHz: FM broadcasting (88-92 non-commercial, 92-108 commercial) 108-118 MHZ: Air navigation beacons VOR 108-132 MHz: Air Traffic Control (AM), 121.5 MHz is emergency frequency 132-144 MHZ: Auxiliary civil services,satellite, space research, and other miscellaneous services 144-148 MHz: Amateur "2-meter" band 148-174 MHz: "VHF Business Band", the new unlicensed Multi-Use Radio Service (MURS), and other 2-way land mobile, FM 156-174 MHz VHF Marine Radio FM 162.40-162.55: NOAA Weather Stations, FM 174-216 MHz: TV channels 7 through 13, and professional wireless microphones (low power, certain exact frequencies only) 216-222 MHz: mixed services 222-225 MHz: Amateur "1-1/4-meter" band above 225 MHz: Federal services, including military aircraft radio (225-400 MHz) AM, including HAVEQUICK UHF brief summary of some UHF frequency usage: 300 - 420 MHz: government use, including meteorology 420 - 450 MHz: radiolocation and Amateur "70 cm" band 450 - 470 MHz: UHF business band, GMRS, and FRS 2-way "walkie-talkies" 470 - 512 MHz: TV channels 14-20, public safety 512 - 806 MHz: TV channels 21-69 (channels 53-69 to be auctioned) 806 - 824 MHz: pocket pagers and Nextel SMR band 824 - 849 MHz: cellular phones, A & B franchises, mobile phone 849 - 869 MHz: public safety 2-way (fire, police, ambulance) 869 - 894 MHz: cellular phones, A & B franchises, base station 902 - 928 MHz: ISM band: cordless phones and stereo, datalinks 928 - 960 MHz: mixed Studio-Transmitter Links, mobile 2-way, other 1240 - 1300 MHz: Amateur radio 1850 - 1910 MHz: PCS mobile phone - note below 1930 - 1990 MHz: PCS base stations - note below note: order is A,D,B,E,F,C blocks. A,B,C = 15 MHz; D,E,F = 5 MHz 2310 - 2360 MHz: Satellite radio Sirius and XM 2390 - 2450 MHz: Amateur radio, shared with below: 2400 - 2483.5 MHz: ISM, IEEE 802.11, 802.11b, 802.11g Wireless LAN around 2450 MHz: Microwave oven |
| Garage
door openers, alarm systems, etc. - Around 40 megahertz Standard cordless phones: Bands from 40 to 50 megahertz Baby monitors: 49 megahertz Radio controlled airplanes: Around 72 megahertz, which is different from... Radio controlled cars: Around 75 megahertz Wildlife tracking collars: 215 to 220 megahertz MIR space station: 145 megahertz and 437 megahertz Cell phones: 824 to 849 megahertz New 900-MHz cordless phones: Obviously around 900 megahertz! Air traffic control radar: 960 to 1,215 megahertz Global Positioning System: 1,227 and 1,575 megahertz Deep space radio communications: 2290 megahertz to 2300 megahertz
2003 US allocation chart 2016 US allocation chart |